Training organisations are getting more creative when it comes to how they help learners. They are working to find techniques, technologies and tools that can include both synchronous and asynchronous learning.
The online learning experience has evolved over the years. The tools used in the past, like e-learning websites, have been replaced by newer technologies that allow for richer experiences for learners – both synchronous and asynchronous ones.
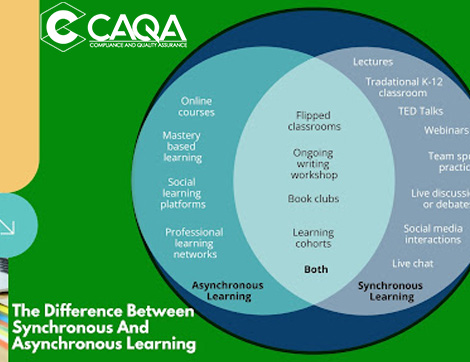
Synchronous learning is an environment in which learners are in the same physical or virtual space at the same time. This includes learning through group discussions, lectures, webinars, etc. One of the main benefits of this type of learning is that it provides opportunities for in-person collaboration and interactions. Synchronous learning can also refer to the traditional classroom setting (face-to-face interaction with a trainer or teaching assistant) where learners are required to attend class in person. In an asynchronous learning environment – as the name suggests – students work together in pairs or groups to receive instruction from one source.
Synchronous learning environments provide opportunities for better relationships between learners and instructors. Synchronous learning is often used in vocational education and training and higher education sectors because it is good for student engagement and relationships which is important to ensure that students come back to training organisations.
Asynchronous learning refers to a different kind of online environment where students are expected to participate remotely, they access instructional learning and training materials each week at any time that best suits them and they do not log in and participate in webinars or class sessions at a specific time each week. Learners have their individualised lesson plans and they interact with other learners and training staff not at all or only for a limited period of time such as asking questions through emails or messages.
Asynchronous environments offer freedom of choice when it comes to when learners can interact with others so they can learn when they want or need to, which can help them complete their studies more quickly. This environment also helps them to learn in different ways depending on how they learn best so they don’t feel overwhelmed by having too much information at a training session or too little information that they feel bored and detached from the learning environment and processes.
The most significant distinction between asynchronous and synchronous learning is the presence of a live instruction component that occurs at a predetermined time.
The difference between synchronous and asynchronous learning environments comes down to when learners complete their tasks. If they are completed during synchronous activities, they are done simultaneously without any interruption from outside forces. If they are completed during asynchronous activities, there are interruptions from time to time which could be due to external factors or individual factors such as someone being distracted or busy with something else.

You can include both synchronous and asynchronous learning through including:
- Flipped classrooms
- MOOCs
- Providing opportunities for learners to attend classes from anywhere
- Communicate regularly with instructors
- Providing access to platforms where people have the opportunity to make connections with other learners
- Providing access to online discussion forums where students can read the discussions and also have the opportunity to participate in the discussion forums as well.